To understand why a company/brand needs to adapt a particular strategy or trend it is essential to know how it functions and will it help your brand for growth, because the ultimate goal of any action taken is to achieve success. Therefore, in this blog we will focus on elaborating the best SEO link practices and how it benefits your content digitally.
Google has recently announced its own version on the Link building best practices. When evaluating the relevance of pages and seeking out new pages to crawl, Google employs links as a signal. Learn how to optimize your anchor text so that both people and Google can understand your material, as well as how to make your links crawlable so that Google can find additional pages on your site via the links on your page.
Links are crucial in the process of SEO, whether they are third-party links or links within your own website because they make the content piece interactive, engaging, and they help build a direct association between the quality/quantity of links to your website and how much search traffic your site obtains.
In simpler words, links are the fuel you need to drive your brand’s vehicle towards its targeted success in the wonderful universe of SEO!
Link building can either be done by naturally obtaining them with the support of exemplary research or by creating engaging content highlighting your brand; at the end, more links result in a higher ranking in SERPS!
Let’s take a look at the link building best practice suggestions from Google:
Crawlable Links
The new google documentation says: “Generally, Google can only crawl your link if it’s an <a> HTML element (also known as anchor element) with an href attribute. Most links in other formats won’t be parsed and extracted by Google’s crawlers. Google can’t reliably extract URLs from <a> elements that don’t have an href attribute or other tags that perform as links because of script events. Here are examples of links that Google can and can’t parse”
Recommended:
<a href=”https://example.com”>
<a href=”/products/category/shoes”>
Not Recommended:
<a routerLink=”products/category”>
<span href=”https://example.com”>
Note from Google: “Make sure that the URL in your <a> element resolves into an actual web address (meaning, it resembles a URI) that Google crawlers can send requests to, for example”:
Recommended (Google can resolve):
<a href=”https://example.com/stuff”>
<a href=”/products”>
<a href=”/products.php?id=123″>
Not recommended (but Google may still attempt to resolve this):
<a href=”javascript:goTo(‘products’)”>
<a href=”javascript:window.location.href=’/products'”>
Anchor Text placement
Use rich anchor text links, per Google’s request. They can learn more about the linked page from this.
According to the documentation: “Anchor text (also known as link text) is the visible text of a link. This text tells people and Google something about the page you’re linking to. Place anchor text between <a> elements that Google can crawl”.
Good:
<a href=”https://example.com/ghost-peppers”>ghost peppers</a>
Bad (empty link text):
<a href=”https://example.com”></a>
This link could be better since there is no anchor text, which is why it doesn’t aid their algorithm in determining the topic of the page. Google will use the title attribute if an anchor text is empty but a link has a title attribute. Here is an illustration of that:
<a href=”https://example.com/ghost-pepper-recipe” title=”how to pickle ghost peppers”></a>
This demonstrates how Google uses the title properties in links to determine how to rank a page. They just prefer that you use links with rich anchor language like:
<a href=”https://example.com/ghost-peppers”>ghost peppers</a>
Additionally, they encourage the usage of alt text for photos, using it as the anchor text when appropriate. Here’s an illustration:
<a href=”/add-to-cart.html”><img src=”enchiladas-in-shopping-cart.jpg” alt=”add enchiladas to your cart“/></a>
Make sure the alt text for your photographs is informative. In this manner, you can increase visitors from Google image search.
How to write good anchor text
Google added yet another new area in the recent doc: “Good anchor text is descriptive, reasonably concise, and relevant to the page that it’s on and to the page it links to. It provides context for the link, and sets the expectation for your readers. The better your anchor text, the easier it is for people to navigate your site and for Google to understand what the page you’re linking to is about.”
Here are a few examples for that:
For a full list of cheese available for purchase, see the <a href=”https://example.com”>list of cheese types</a>.
Google also mentioned that they don’t want you to write long and lengthy anchor texts, for example, this is too descriptive & not recommended by Google:
<a href=”https://example.com”>Knitted Cow invites local residents of Wisconsin to their grand re-opening by also offering complimentary cow-shaped ice sculptures</a> to the first 20 customers.
Rather you they prefer something like this:
<a href=”https://example.com”>Knitted Cow invites local residents of Wisconsin</a> to their grand re-opening by also offering complimentary cow-shaped ice sculptures to the first 20 customers.
In Google’s policy, keyword stuffing is mentioned as a prohibited practice. Thus, in order to succeed, you don’t need to include too many keywords in the anchor text. Additionally, one word anchor texts are too general and don’t benefit Google sufficiently.
Internal Linking for SEO
No set number of links is required, according to Google, which says: “You may usually think about linking in terms of pointing to external websites, but paying more attention to the anchor text used for internal links can help both people and Google make sense of your site more easily and find other pages on your site. Every page you care about should have a link from at least one other page on your site. Think about what other resources on your site could help your readers understand a given page on your site, and link to those pages in context.”
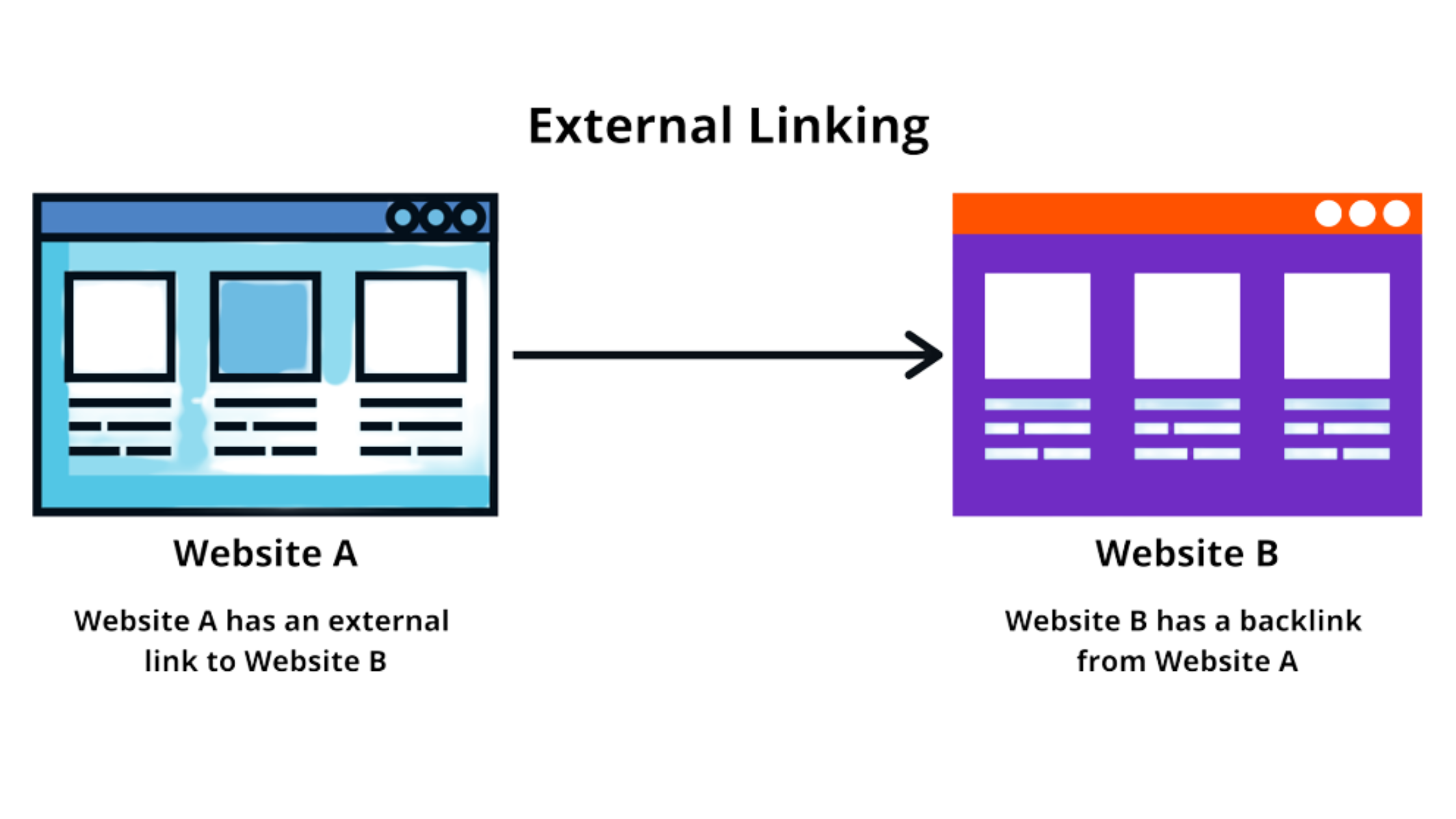
External Linking for SEO
According to the doc: “Linking to other sites isn’t something to be scared of; in fact, using external links can help establish trustworthiness (for example, citing your sources). Link out to external sites when it makes sense, and provide context to your readers about what they can expect.”
In simpler words, google does not want them too close or similar to each other, for example:
I’ve written about cheese
<a href=”https://example.com/page1″>so</a>
<a href=”https://example.com/page2″>many</a>
<a href=”https://example.com/page3″>times</a>
<a href=”https://example.com/page4″>this</a>
<a href=”https://example.com/page5″>year</a>.
For them, it is not ideal.
You should space out your links by at least a few words, if not a sentence or two. Here is the more suitable illustration that they provided.
I’ve written about cheese so many times this year: who can forget the
<a href=”https://example.com/blue-cheese-vs-gorgonzola”>controversy over blue cheese and gorgonzola</a>, the <a href=”https://example.com/worlds-oldest-brie”>world’s oldest brie</a> piece that won the Cheesiest Research Medal, the epic retelling of <a href=”https://example.com/the-lost-cheese”>The Lost Cheese</a>, and my personal favorite, <a href=”https://example.com/boy-and-his-cheese”>A Boy and His Cheese: a story of two unlikely friends</a>.
In short, Internal and external links are encouraged by Google since they aid in the decision-making process for how to rank websites.
Google still encourage you to utilize rich anchor text, for instance, when you use internal links to link to other pages on your website.
They make it clear that the anchor language ought to be understandable enough for users to understand what they are clicking on and the purpose of the linked page.
Google is in the same position. They should be able to comprehend the purpose of the connected page from the internal link’s anchor text as well.
Conclusion
Google advises you to create links like mentioned below if you want to rank well:
- Strong anchor text enhances your rankings because it contains keywords.
- Short anchor text is preferred because Google doesn’t like extensive anchor text.
- Use alt text; it takes the role of anchor text for images.
- Use title attributes because Google uses them to identify anchor text.
- Spread out your links; ideally, there should be a few words or even a few lines between each one.
- Use internal links. While you shouldn’t disregard external links, which are the focus of most SEOs, internal connections are a simple approach to improve your ranks.